Physical features are natural landforms found on the surface of the earth.
They include;
1. Mountains and Highlands
2. Ranges
3. Hills
4. Plains
5. Seas
6. Plateaus
7. Oceans
8. Depressions
9. Valleys
10. Escarpments
11. Rivers
12. Lakes
13. Swamps
14. Islands
Physical features can be divided into two major groups namely:
These include mountains, hills, highlands, basins, valleys and plains.
Include: rivers, streams, lakes, swamps, dams, oceans and seas.
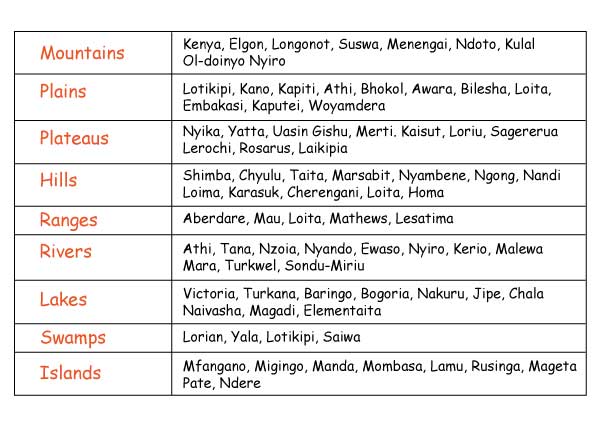
The map below shows the relief features of Kenya.
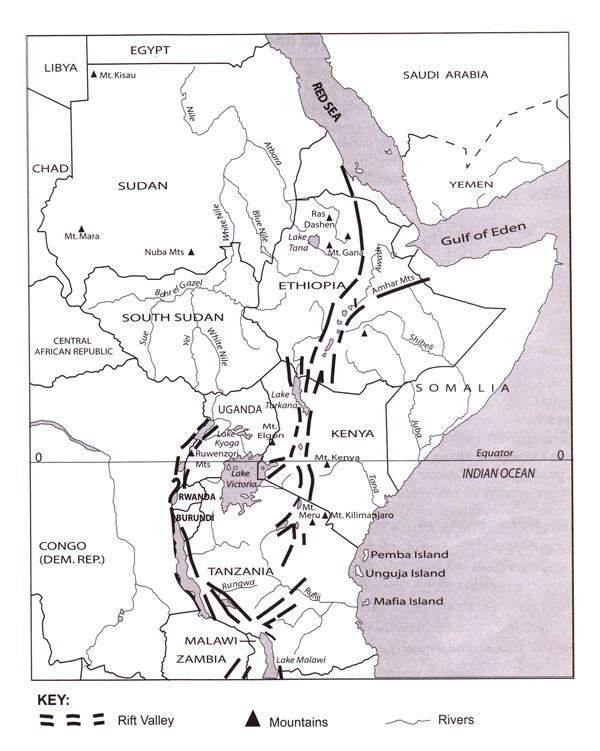
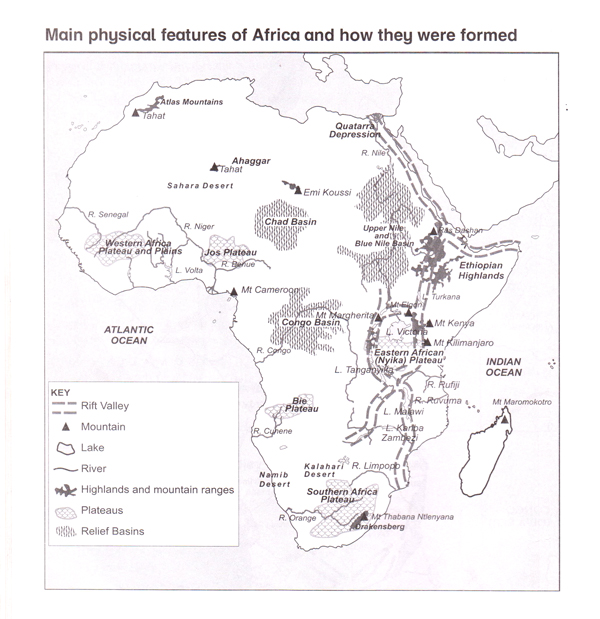
The map below shows the physical features of Africa
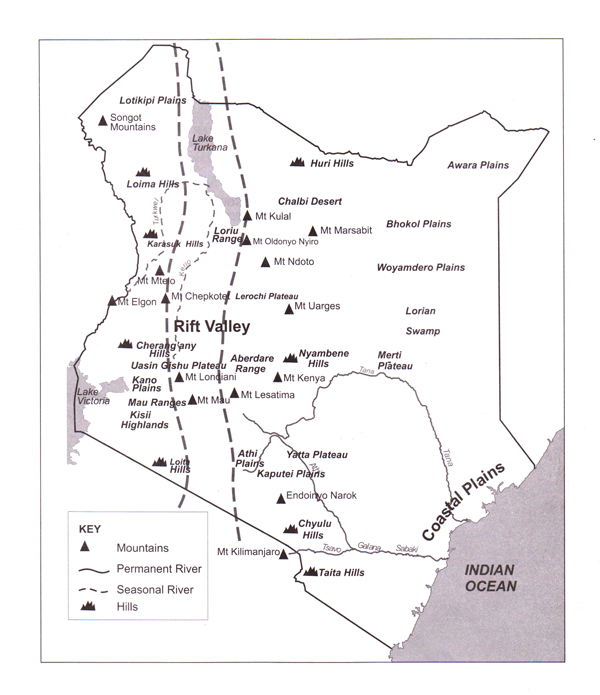
This feature is about 7 200 km long.
In Africa, it stretches from the Red sea, South West across Ethiopia and South into Kenya, Tanzania and Malawi to Beira in Mozambique.
The Great Rift Valley ranges in elevation from 400m below sea level to 1900m above sea level in Southern Kenya.
Watch the Rift Valley video below
Mountains in Africa are classified according to how they were formed. Mountains are grouped into four main types namely:
Mount Kilimanjaro is the highest mountain in Africa.
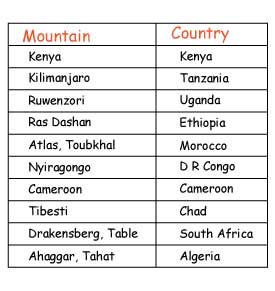
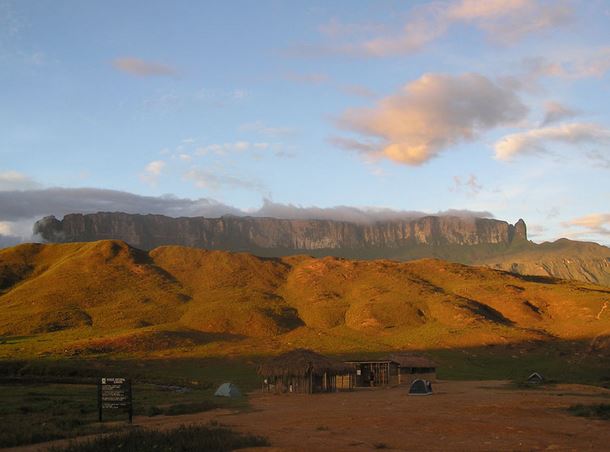
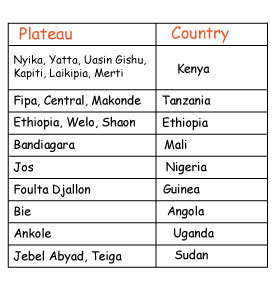
This is a high area that has an almost flat or level surface with steep slopes. It is sometimes called a tableland.

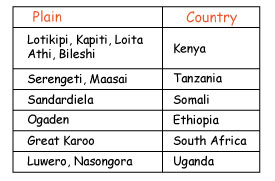
These are flat, low-lying and gentle sloping regions.
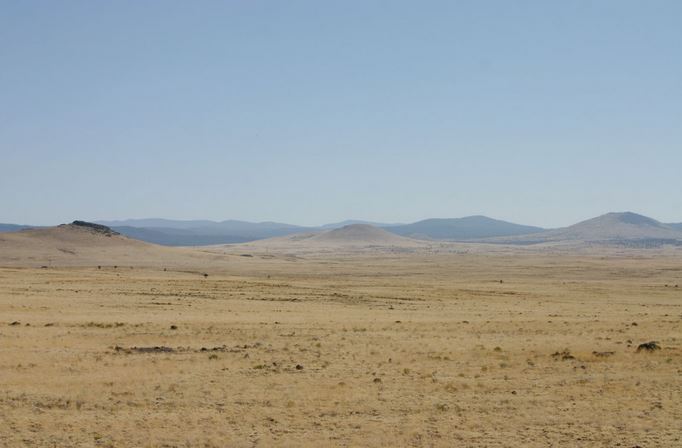

These are lowland areas separated by plateaus and mountains. Some have lakes in the lowest parts.
They include;
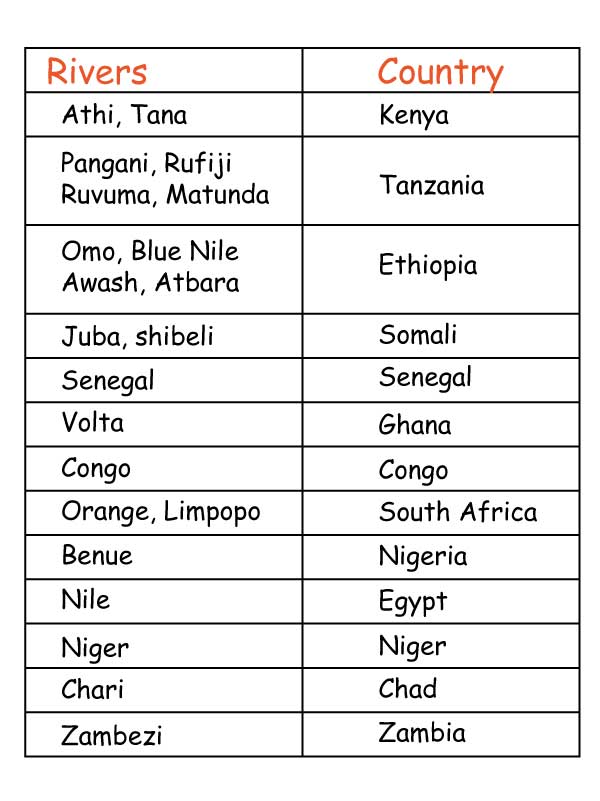
A river is a stream of moving water flowing in a channel.
A point where a river begins is its source. This may be a lake, spring, melt water from ice or a highland region receiving high rainfall.
Smaller streams joining the main river are called tributaries. A point where two tributaries come together is called a confluence.
A river, together with its tributaries, form a river system. Each river system drains through a drainage basin. A highland area that divides two or more river systems is known as a watershed.
A point at which the river ends is its mouth. A river mouth may be in form of a single narrow stream called an estuary, or it may split into smaller streams called distributaries to form a delta.
Examples of rivers that end in estuaries in Africa are Rivers;
Those that end in deltas include Rivers;
Rivers in Africa drain into the following;
Lakes are depressions on the surface of the earth which are filled with water. Some lakes have fresh water while others have salty water. Some lakes are big while others are small. Below is an image of Lake Turkana, a large salt lake.

Fresh water lakes usually have inlets as well as outlets.
As a result, the amount of salt in the water is reduced.
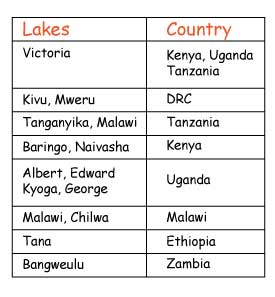
Examples of fresh water lakes in Africa are Lakes Victoria, Kyoga, Tanganyika, Turkana, Baringo, Albert, Edward, Malawi, Naivasha and Tana.
Fresh water lakes in uganda
Salty-water lakes do not have outlets. Water comes into the lake but very little goes out.
Instead, water is mainly lost through evaporation. This leaves behind a lot of salt in the water.
Salty-water lakes are important sources of salt and soda ash.
Examples of salt water lakes in Africa include Lake Magadi, Elementaita, Nakuru, Bogoria, Amboseli, Bangweulu, Chad, Eyasi and Natron.
Lakes and the Rift Valley
Some lakes are found outside the Rift Valley while others are found within the Rift Valley.
Lakes which are found outside the Rift Valley are lakes;
Lakes and the Rift Valley
Lakes found within the Rift Valley include:
Kenya: |
Turkana | Nakuru | Logopi | Baringo | Elementaita | Naivasha | Magadi |
Tanzania: |
Natron | Manyara | Eyasi | Makati | Kivu | Tanganyika | Rukwa |
Uganda: |
Albert | Edward | Bunyoni |
Swamps
a) Swamps are found in areas that are generally fl at, making it easy for water to flow into them.
b) It is diffi cult for water to drain away. Such areas have clay soils, which do not allow water to seep through them easily.
c) Swampy areas are usually found along the coast or around lakes.
d) They are covered with swamp vegetation like reeds and papyrus if the water is not salty.
e) Mangrove swamps are found along the coast where the water is salty.