- Vegetation refers to the different plants found in a place.
- Natural vegetation is the plant cover that grows in a place under natural conditions.
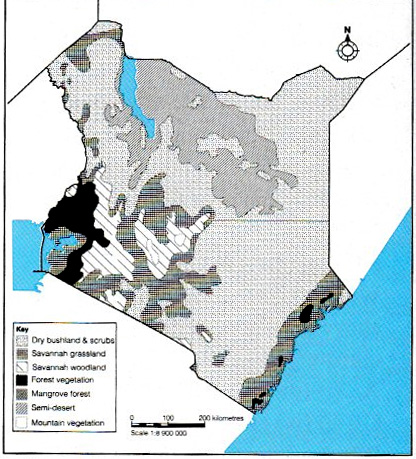
a) Vegetation in Kenya
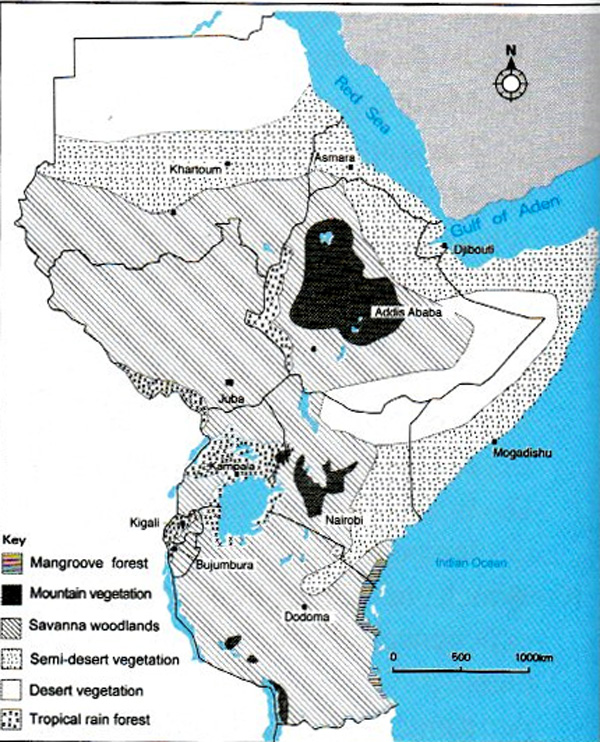
b) Vegetation in East Africa
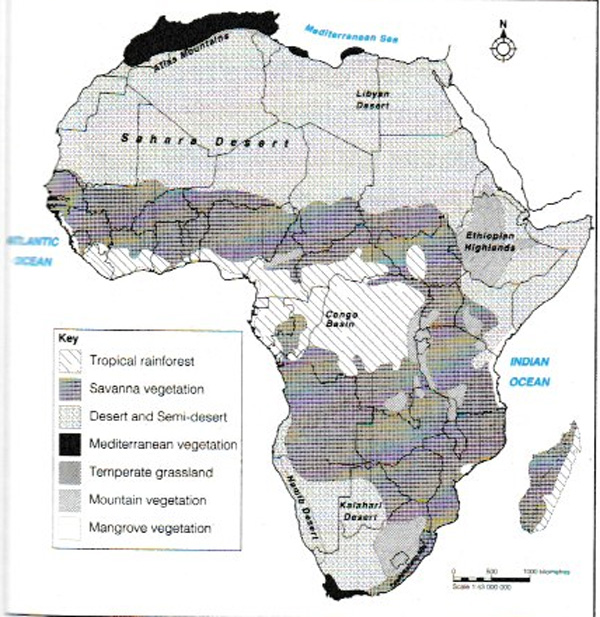
c) Vegetation in Africa
- Planted vegetation includes what has been planted by people like maize, coffee, bananas and tea.
- Here is an example of planted vegetation - a coffee plantation in Ecuador.

1. Tropical rain forest.
2. Savannah (Tropical grasslands).
3. Desert and semi-desert vegetation.
4. Mediterranean vegetation.
5. Temperate grassland.
6. Mountain vegetation.
- These forests are also known as equatorial rain forests.
- They are found in areas that experience equatorial climate.
- These areas include parts of the coastal regions of West Africa, the Congo Basin in Central Africa, Southern parts of West Africa, and a few lowland parts of Eastern Africa.

Main characteristics of the tropical rain forest
- This type of vegetation is found in areas that experience tropical continental climate bordering equatorial forests.
- Tropical or sub-tropical grassland lying on the margin of the trade wind belts.
- These areas include parts of the Coastal regions of West Africa, the Congo Basin in Central Africa, Southern parts of West Africa, and a few lowland parts of Eastern Africa.

Main characteristics of tropical savannah
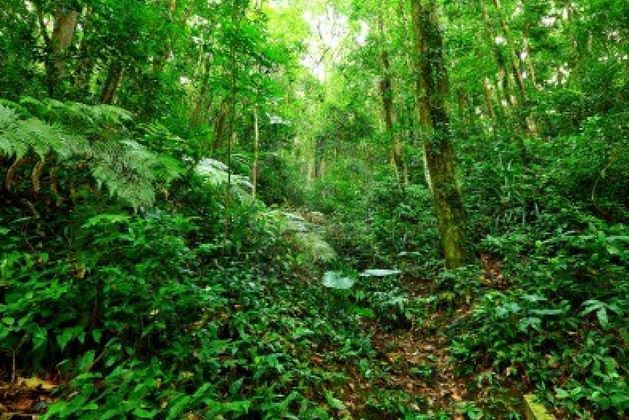
- Desert and semi-desert areas are found in deserts.
- These are areas that receive very little or no rainfall.
- As a result, the vegetation is very poor.
- Desert and semi-desert vegetation consists of small thorny bushes which take very long to grow.
- The vegetation is scattered and stunted.
- The plants have thick stems for storing water. The stems are also fleshy thick backs to store water.
- Long roots to tap water from underground.
- The leaves are waxy, shiny and thin. This helps them to control the amount of water they loose through transpiration.
- The common plant that is found in this region is cactus.

- Most trees have no leaves throughout the year.
- Shrubs shed off their leaves during the dry season.
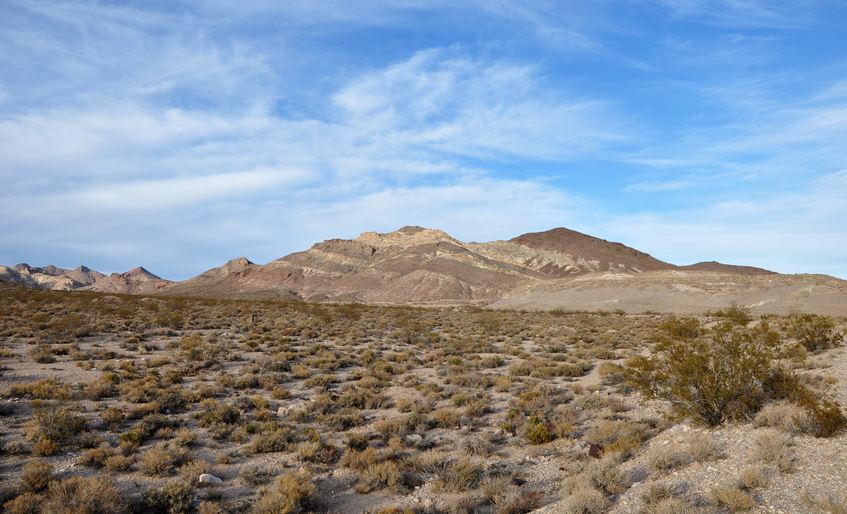

- This vegetation is found in the Northern and Southern tips of Africa.
- These areas have hot and dry summers and winters. Plants here have adapted well to the climate.

- The main vegetation here is woodland and shrub. Some plants are short with woody stems.
- Other plants that are found here are short sweet-smelling herbs like lavender, rosemary and thyme.
- Plants have thin and shiny leaves to reduce water loss.
- Trees have thick barks and deep roots.
- Most trees have a conical shape.
- It is made up of coniferous softwoods like pine and beech.
- These are mainly found in temperate regions of Africa, especially in the Central part of South Africa where they are known as the veld.
- These areas have a cool climate, sometimes with severe winters.
- During summer, the grass grows quickly and forms important pastures for both dairy and beef cattle.
- However, the height of the grass depends on the amount of rainfall received. Near the Kalahari Desert, the grass is short and scattered.

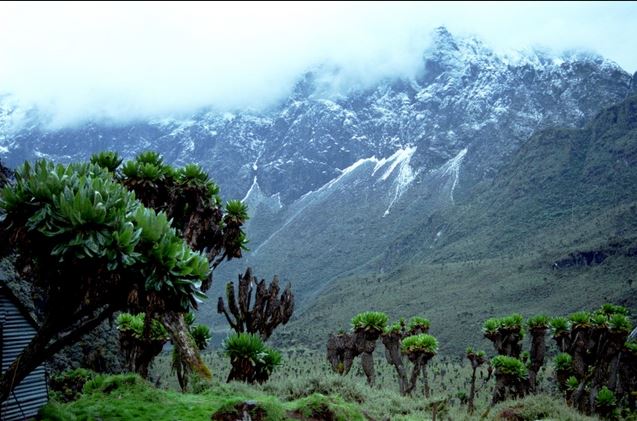
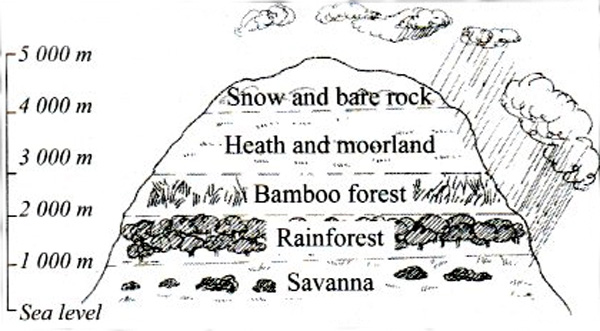
- On mountains, the windward slopes receive more rainfall than the leeward slopes.
- As a result, vegetation is richer. As one moves up the mountain, vegetation changes too.
- The vegetation at the top of high mountains is called heath and moorland. This consists of short grass that is adapted to the cold conditions at the top.
- Very high mountains like Mt. Kenya and Kilimanjaro have no vegetation at the top because they are covered with snow and ice.

- These are forests found along parts of the coast.
- They grow in shallow sheltered parts of the sea where the sea penetrates into the land or shallow river mouths.
- The forest grows in shallow waters, they have breathing roots and they are adapted to salty water.
Distribution of vegetation is influenced by the following factors:
a) Climate: High rainfall and temperatures
support plant life. Forests are found in
such areas.
b) Distance from water bodies: Places away from water bodies have poorer
vegetation.
c) Relief: As one moves up the mountain, the vegetation changes because of change in temperature and rainfall amount.
d) Human activities: Natural vegetation is cleared by people for settlement and
cultivation.
e) Soils: Sandy soils have poor vegetation because they do not hold enough water. Clay soils are waterlogged and have swamps because water does not drain easily through them.
f) Government policy.
Vegetation is an important natural resource. Therefore, we must take care of it. Below are some ways in which vegetation is important to us.
a) Forests protect mountain areas where rivers begin.
b) Wild animals live in grasslands and forests. They also need plants for food.
c) Trees are used to make timber and paper.
d) Some trees in the forest provide us with fruits. Fruits are a good source of
vitamins.
e) Some trees in the tropical rainforests provide important products like cocoa,
rubber and palm oil. These are exported to other countries.
f) Some plants are used to treat different kinds of diseases.
g) Grass is used to thatch houses.
h) Papyrus trees and reeds from swamps provide material which is used to make furniture, baskets, and mats. They also provide poles for building houses.
i) Plants growing in swamps help to clean and purify water.
j) Flowering plants provide nectar for bees. Bees use it to make honey.
k) Savannah grasslands are important wildlife conservation areas where tourists visit to see wild animals. This earns the countries money.
l) Vegetation makes a place look beautiful to look at and to live in.