- Plants are living things.
- Some plants are big and others are small.
- We can climb big plants.
- Most plants have green leaves.
- We eat some plants.
- Plants we eat are called edible.
- Plants give us food, medicine, shade and timber.
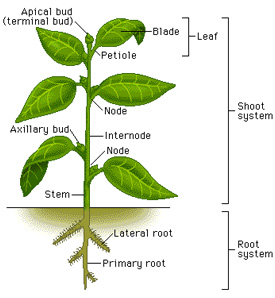
The parts of a plant include:

- Roots
- Bud

- Flowers
- Leaves
- Stem
- Fruit
- Edible parts of a plant
- Leaves we eat
- Roots we eat
Fruits we eat
Stems we eat
We eat the stem of sugarcane
Seeds we eat
Plants make food in the leaves.
Seeds are found inside the fruit.
Fruits grow from flowers.
Some fruits like watermelon, passion and pawpaw have many seeds.
Mango and avocado fruits have one big seed.
A tomato is a fruit as well as a vegetable.
The Root Roots of a plant are found below the ground (in the soil).
1. To anchor the plant firmly in the soil

2. To absorb water and nutrients from the soil and passes them to the stem.
3. In some plants such as carrots and cassava, the roots are used to store food.

4. To help in the taking in of air by plants like the mangrove.
These roots are breathing roots

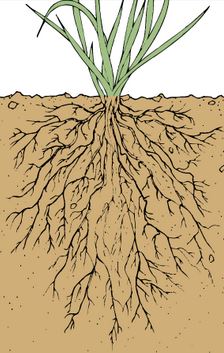
There are two types of roots: the tap root and the fibrous root.
Include taproots and fibrous root.

Taproot
The taproot is the main root which grows from the radicle and continues to grow bigger than its branches.
It grows vertically down into the soil, producing smaller side branches.
Most dicotyledonous plants have this type of root.
The best example is the carrot.

Fibrous roots have no main root.
Instead all the roots grow to almost the same size.
The roots grow from the base of the stem and spread into the soil.
Most monocotyledonous plants have fibrous roots.
An example is maize and grasses.
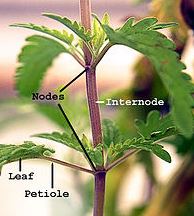
The stem performs the following functions:
1. It supports the other parts of the plant (leaves, flowers and fruits)
2. It helps in transporting water and dissolved nutrients from the roots to the other parts of the plant
3. Transports food that is made in the leaves to the roots for storage
4. Stores food in plants like sugarcane.

The functions of the leaves are:
1. Manufacturing food in a process of photosynthesis using chlorophyll, sunlight, carbon dioxide and water
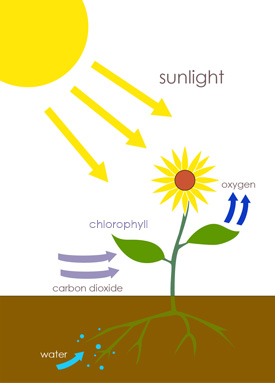
2. Trapping sunlight for photosynthesis
3. Absorbing carbon dioxide from the air and releasing waste (oxygen) into the air
4. Storing food in some plants like onion

5. Helps in transpiration (losing of excess water from the plant), through the stomata.
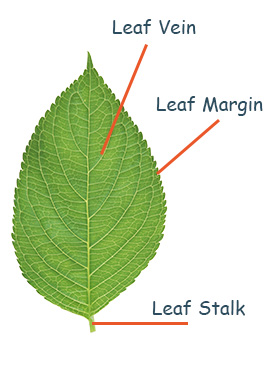
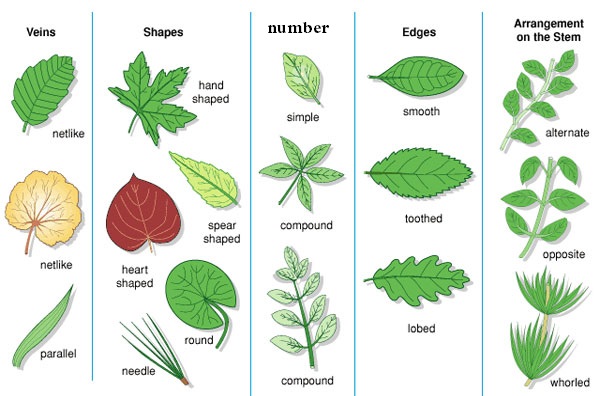
Leaves can be grouped in different ways.
They can be grouped according to their colour, size, shape and texture:
Colour: some plants have green leaves, others do not.

Plants that do have green leaves are green plants while those that do not have green leaves are non green plants.
Size: some plants have small or tiny leaves for example groundnut plants and pine, while other plants have large leaves for example bananas and arrowroots.

Some leaves are broad for example kales (sukuma wiki) leaves while others are narrow for example sugarcane leaves.
Shape: leaves can be grouped according to different shapes.
Leaves are pin-shaped, round, heart shaped, palm shaped and sword shaped.


Types of leaves
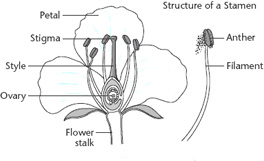
Flower is the reproductive part of the plant.
Parts of the flower are:
1. Petals are coloured and have scent. Their function is to attract insects for pollination. Petals are collectively called corolla.
2. Sepals are often small and green. Sepals protect the young flower when in bud. Sepals are collectively called calyx.
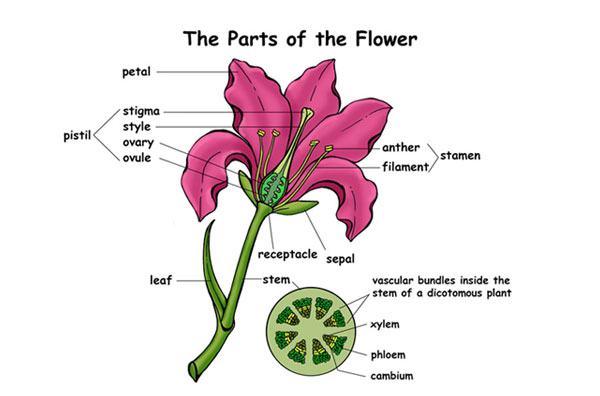
3. The stamen is the male part of the flower.
It is made of the filament and anther.
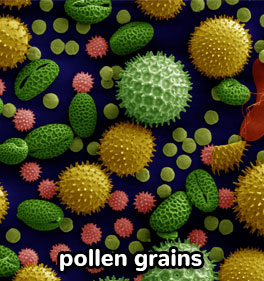
The anther produces pollen (the male sex cells).
The pollen grains are held in pollen sacs, in the anther.
4. The pistil is the female part of the flower.
It is made of the stigma, the style, and the ovary.
The ovules (the female sex cells) are produced and held inside the ovary.
The style is the tube that connects the stigma to the ovary.
The stigma receives pollen.

5. The nectary is the part of the flower that produces nectar.
The nectary is located near the ovary.
1. Most of the transpiration in a plant takes place from the
A. Flowers B. Leaves C. Roots D. Stems
2. Fatuma covered a leafy branch of a potted plant with a dry polythene bag as shown in the diagram below.
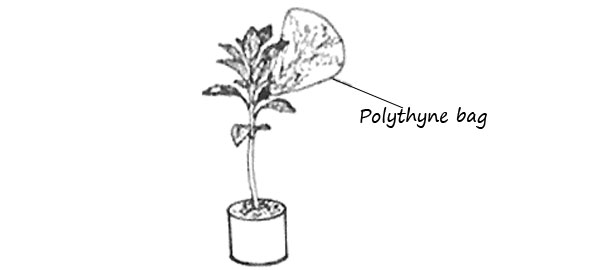
She observed water droplets forming inside the bag after leaving the set-up in the hot sun for some time.
Water droplets appeared in the polythene bag due to
A. Transpiration and condensation B. Evaporation and condensation
C. Photosynthesis and evaporation D. Evaporation and saturation
1. Which one of the following types of roots are found in onion plants?
A. Fibrous roots B. Adventitious roots
C. Prop roots D. Tap roots