- The sky is the region high above the earth’s surface.
- During the day, we can observe the sun and the clouds in the sky.
- During the night we can observe the moon, the clouds and the stars.
- The sky changes during the day and during the night.
- In the morning, the sun rises from the east and it is not so bright or so hot.
- But at midday, the sun is in the overhead position in the sky.
- At this time,the sun is so bright and also very hot.
- In the evening the sun is not so bright as it sets in the west.

- Though it seems as if the sun moves, it is the earth that goes round the sun.
- The earth revolves around the sun.
- The earth takes 365 days to go round the sun once (to make one complete revolution).
- At night, the stars and the moon glow and can be seen because during the day the sun is more bright.
- They project their light from the sun.
- The moon changes its shape as the days go by.
- It starts as a new moon which is not visible to the eye.
- During the days that the new moon is in the sky, the nights are dark.
- After some days, the moon increases.
- The shape that is seen immediately after the new moon is a crescent
- From the crescent, the moon further increases in size and becomes a first quarter.
- The shape is half a circle.
- By this time the sky starts becoming clear at night.
- When the moon increases its shape again it becomes a gibbous.
- From the gibbous it becomes a full circle and is referred to as a
full moon.
- When the moon is full in the sky,the night becomes brighter and clearer.
- From full moon, the moon decreases in size to a gibbous, then last quarter, crescent and finally becomes a new moon.
- This cycle repeats itself regularly.
There are different types of clouds.
The clouds are classified depending on how high they are in the sky and according to their shapes.
The clouds can tell what kind of weather to expect.
The types of clouds are:
These clouds are white in colour.
They look like bundles of cotton wool with a flat bottom.
They are usually high up in the sky.
These clouds are dark grey in colour.
They do not have a specific shape and are usually low in the sky.
They bring about rain and are called rain clouds.
These clouds look like feathers and they form very high up in the sky.
Weather and the solar system
Standard 4
1. The chart below shows records of weather made by pupils in Standard IV each day for a week.
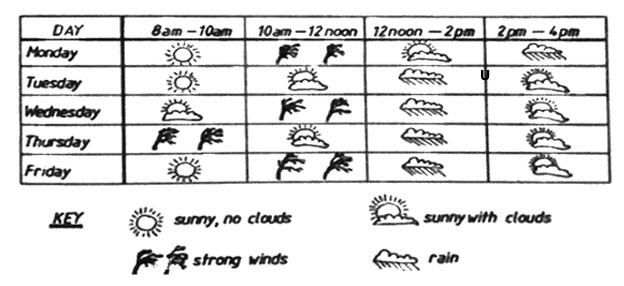
Which of the following statements is correct about the chart above?
A. It never rained without strong winds blowing first.
B. Rain in the afternoon always stopped before school closed at 3:30 p.m.
C. It was sunny with no clouds at some time every day.
D. It was always wetter in the afternoon than in the morning.
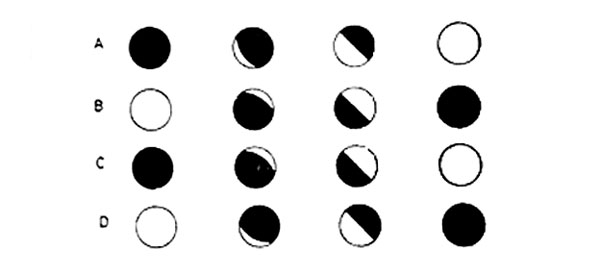
2. Which one of the following CORRECTLY shows the phases of the moon starting from the new moon until the full moon?
3. Children at Hanga Primary School made weather observations for one week and recorded them as shown in the table below.
|
DAY |
TEMPERATURE |
WIND DIRECTION |
RAINFALL |
|
Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday Sunday
|
HOT COLD COLD HOT COLD COLD HOT |
NORTH SOUTH NORTH WEST SOUTH WEST NORTH |
HEAVY RAIN HEAVY RAIN HEAVY RAIN NO RAIN NO RAIN HEAVY RAIN HEAVY RAIN |
Which one of the following conclusions can be made from the table?
A. It never rained on a cold day
B. It always rained when the wind blew from the North
C. It never rained on hot days
D. It always rained on hot days
4. The chart below shows a record of weather made by pupils in Standard Five for a week.
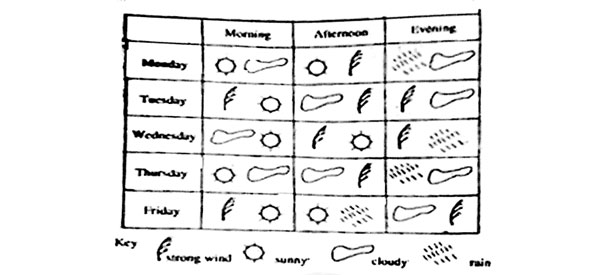
Which one of the following statements about the weather chart above is correct?
A. It only rained after strong winds blew earlier in the day.
B. It was cloudy in all afternoons.
C. It was sunny every day in the morning and windy every day in the afternoon.
D. Strong winds blew in the mornings on more days than in the evenings.
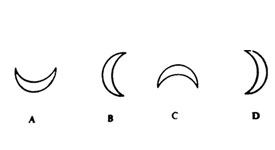
5. Which one of the following shapes of the moon is observed after the new moon?
6. Under which one of the following weather conditions would clothes dry the fastest? Hot and
A. Humid B. Dry C. Calm D. Windy
1. What is the name given to the kind of clouds which most often give rise to rain?
A. Cirrus B. Cumulus C. Nimbus D. Stratus