The Organisation of African Unity (OAU) and African Union (AU)
During the 1960’s, many African states were beginning to get their independence and they saw the need to unite politically and economically.
It was out of this need that OAU was formed.
The OAU was formed in Ethiopia in 1963 and its headquarters is in Addis Ababa. Every independent sovereign African State is entitled to become a member of OAU.
The founding members of the OAU
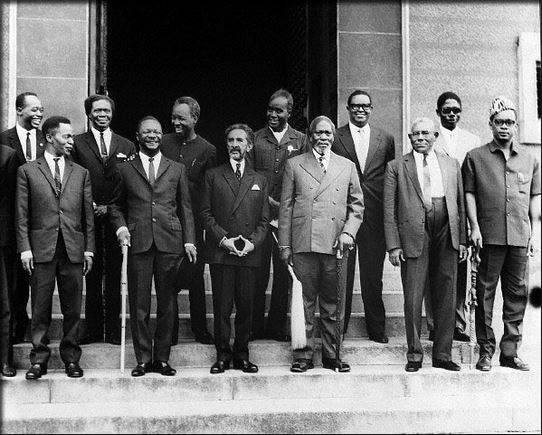

Functions of OAU
In order to achieve these objectives the member states agreed on general policies, especially in the areas of:
- Politics and diplomacy
- Money and the economy
- Education and culture
- Health, sanitation and nutrition
- Science and technology
- Defence and security
The organisation holds the following principles:
- All member states should have equal power
- States should not interfere in the internal affairs of other states.
- Members should respect each state and its rights to independence
- Arguments should be setted peacefully by negotiation
- A 'policy of nonalignment' - member states should not form exclusive agreements with other states
Achievements of OAU
- It helped some African countries to gain independence.
- It has resolved conflicts over boundaries between many African countries and restored peace through its peace army.
- It has promoted trade.
- It has united African countries.
- It helped stop apartheid in South Africa.
- It promoted education, health and science in the continent.
- It promoted international understanding.
Problems that faced OAU
- Some of the member countries did not pay their contributions on time.
- Different countries followed different political ideologies and this dicouraged the development of strong trading ties among member states.
- OAU member countries lacked unity among themselves.
- It lacked a peace keeping force to resolve conflicts and wars in the region.
Formation of AU
At a Heads of state meeting in Johannesburg, South Africa, a decision was made to change the name of OAU to the African Union, or AU.
Objectives of AU
- To promote unity and co-operation among member states.
- To improve the standards of living of the people of Africa.
- To help all African countries to attain independence.
- To defend independence of African States.
- To eradicate all forms of colonialism from Africa.
- To promote international co-operation.
- To promote good governance in Africa
- To promote security in areas of conflict in Africa.
- To promote trade among African countries
- To promote and improve human rights in the country.
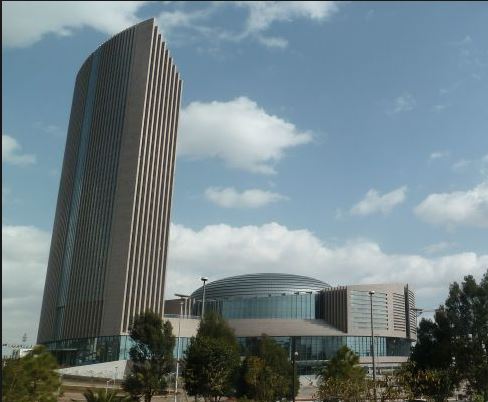
Below is an image of the AU headquarters in Addis Ababa

And here is a photogaph from inside the AU headquarters, during a meeting.

The United Nations (UN)
In 1939, the Second World War broke out.
During the war, in 1941, the president of the United States of America, Franklin Roosevelt and the British Prime Minister, Winston Churchill held a meeting which became known as the Atlantic Charter.
They came up with the idea of an international organisation to monitor and maintain peace in the world.
Another meeting was held in Moscow in 1943 and was attended by representatives from Britain, Soviet Union, China and USA.
These people signed a declaration supporting the idea of an international organisation.
The following year (1944), representatives from the same countries met again in Washington DC and worked out a set of laws for the organisation.
In April 1945, delegates from fifty countries met in the first United Nations Organisation Conference.
In June the same year, they discussed and approved the laws to govern the organisation.
On 24th October 1945 the laws were signed by all the nations that supported the new organisation. By 2004, the UN had 191 member countries.
Here is the inside of the UN General Assembly in New York

Reasons for the formation of The United Nations (UN)
United Nations was formed after the Second World War which ended in 1945. Below are the main reasons why it was formed:
- To maintain international peace and security.
- To achieve international co-operation in solving economic, social, cultural and humanitarian problems.
- To improve living standards of people around the world.
- To create awareness regarding basic human needs such as shelter.
- To help solve international disputes.
- To support the process of decolonisation and achievement of independence.
FUNCTIONS OF SELECTED AGENCIES OF THE UN
United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR)
UNHCR was set up in 1951.
UNHCR recognises that refugees have rights which must be protected and lays down minimum standards of how refugees should be treated.
It also has the following functions;
- Co-ordinating help and relief supplies to refugees.
- Providing refugees with food, shelter, clothing and medical care.
- Providing training to refugees to enable them to become self-supporting.
- Encouraging refugees to return to their countries once there is stability.
- Supporting and funds resettlement and integration of refugees into their countries.
This image shows an example of a UNHCR refugee camp.
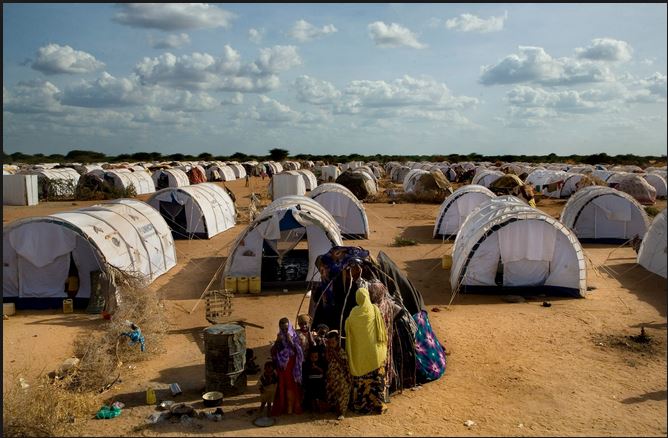

United Nations International Children’s Fund (UNICEF)
UNICEF was formed in 1953. Its main aim is to fight disease, malnutrition and illiteracy among children.
It aims at making the world a place where the rights of every child are realised. UNICEF believes that by caring for children people will to some extent, overcome challenges like poverty, malnutrition, violence, disease and discrimination.

UNESCO
United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation was established in November 1945.
The main aim of establishing UNESCO was to promote international collaboration in the areas of education, science, culture and communications.
Its main goal is to ensure that people respect justice and rule of law.
UNESCO supports the following:
- Freedom of the press and other forms of media.
- Promotion of cultural diversity.
- Preservation of human rights.
- Preservation of the world’s heritage sites.
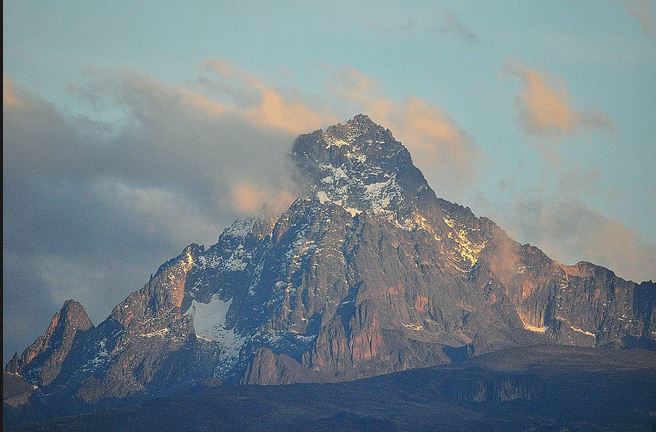
One example of a World Heritage Site - an area which UNESCO believes should be protected, is Mount Kenya.
Mount Kenya is shown in the image below.

WHO
World Health Organisation was formed in 1948 and has its headquarter in Geneva, Switzerland.
WHO's main aims are to;
- Provide governments with advice and assistance to strengthen national health services.
- Provide trained health workers.
- Eradicate major diseases like malaria, smallpox, tuberculosis, leprosy, swine Flu and HIV and AIDS.
- Sponsor programmes related to promoting healthy living through eating healthy foods and observing hygiene.
- Protect the health of mothers and children.
- Improve sanitation and water supply.
- Promote mental health.
- Promote medical research.
FAO
“Let there be bread” is the motto of the Food and Agriculture Organisation. The main objective of FAO is to assist nations of the world to be free from hunger. FAO assists in the improvement of production and distribution of food and agricultural products.
It helps developing countries to use modern methods in order to improve food production in agriculture, forestry and fisheries.
It works towards ensuring that there is good nutrition and food security for all.
By 2008, it had a total of 191 members.
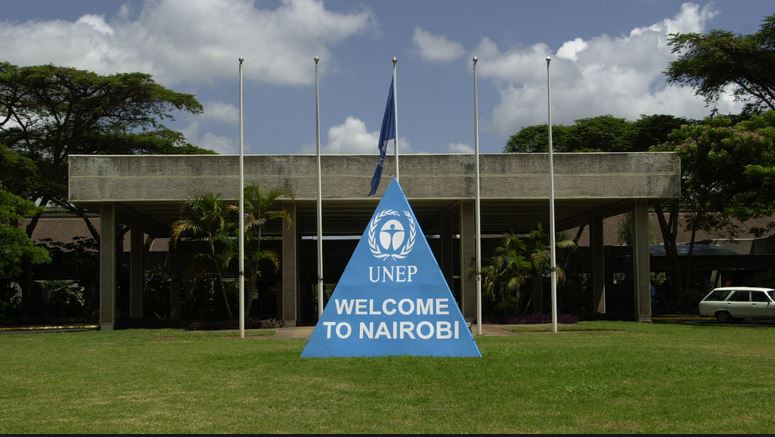
UNEP
United Nations Environmental Programme (UNEP) was founded in June 1972 and its headquarters are in Nairobi, Kenya.
UNEP monitors changes in the environment.
It co-ordinates activities aimed at promoting proper use of the environment.
It brings to the attention of the world environmental issues affecting the earth with the view to finding solutions to them.
It is mainly concerned about global pollution which in a way is contributing to global warming.
Its main areas of concern are:
- The atmosphere
- The oceans, seas and lakes
- Land
Here is a photograph of the UNEP headquarters in Nairobi.

WFP
World Food Programme was established in 1960. Its main objectives are:
- To save lives by providing food to people in refugee camps and those under other difficult circumstances such as floods and drought.
- Improve the nutrition and quality of life of people whose lives are in danger.
- Establish programmes that assist especially poor people to become self-reliant.
- To fight malnutrition that causes death in children.
- To establish Food-for-Work programmes that promote food production
World Bank
It was set up in 1944 and has its headquarters in Washington DC.
The World Bank is made up of two main institutions:
- The international Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD)
- International Development Association.

The World Bank lends money to developing countries to help them meet some of their basic needs.
It also lends money to groups of people interested in improving the environment.
It has given money towards activities aimed at achieving the following:
- Eradicating hunger
- Achieving Free Primary Education
- Promoting gender equity and empowering women.
- Improving health of mothers
- Reducing infant mortality
- Fighting HIV and AIDS and other diseases
- Controlling deforestation
Problems facing the UN
- The organisation lacks the mechanism to implement resolutions.
- Lack of adequate funds to finance its operations.
- Failure by poor nations to repay their loans, leading to debt crisis which cripples the activities of the organisation.
- Lack of a standing army to maintain peace in the world.
- Disagreement among member states over leadership at the Secretariat.
The Commonwealth
The Commonwealth is an association of 53 countries which have experienced a direct or indirect rule by the British.
Most members are former British colonies.
The oldest members are Britain, Canada, Australia and New Zealand, which became independent before 1914.
Recent members are the former British colonies in Asia, Africa and the Caribbean. Kenya joined the Commonwealth in 1963 when it became independent.
The head of the Commonwealth is the British Monarch who by 2013 was Queen Elizabeth II.
Here is a map showing the members of the Commonwealth
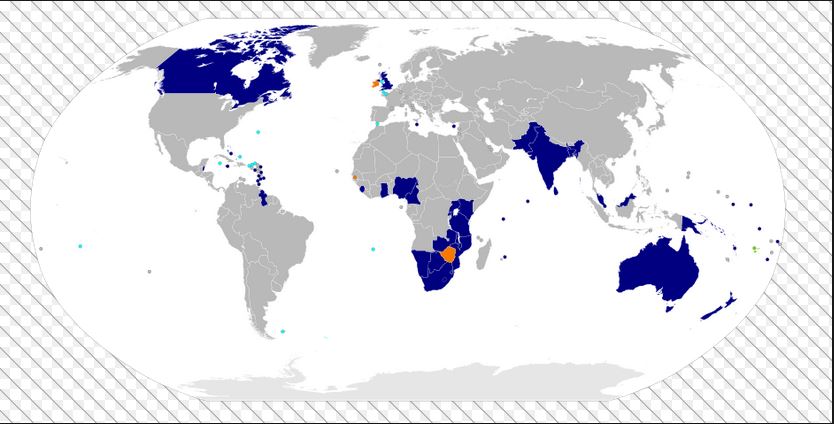
Reasons for the formation of the Commonwealth
The Commonwealth was formed in order to:
- Support good governance and promote principles of democracy.
- Promote international understanding amongst member states.
- Support the education of the children from the Commonwealth country by giving scholarships.
- Eradicate poverty among member states.
The main functions of the Commonwealth
- Promote co-operation among its members.
- Support education in member countries by giving Commonwealth scholarships to bright students to study in other Commonwealth countries.
- Promote international understanding among member states. This is accomplished through the various forums such as the Commonwealth Games, summits and other meetings
- Promote friendly relations and unity when the leaders from member countries meet to discuss important matters about their countries.
- Support functions of the UN, both financially and in other ways like providing peace keeping forces.
The main functions of the Commonwealth
- Promote the principles of democracy, good governance and human rights.
- Send election observers to ensure that the elections are free, fair and democratic.
- Support the work of governments and non-governmental organisations that deal with poverty eradication.
- Produce publications on issues such as environmental degradation, democracy, good governance, human rights and trade.
- Provide training services for professionals
- Set up the Commonwealth Fund for Technical Co-operation which is used to finance activities that promote technical co-operation in the developing countries that are members of the Commonwealth.
The Commonwealth Games help to promote realtions between member countries











