| Democracy and Human Rights |
|---|
| Forms of child abuse |
| Human rights education - KNHCR |
| Bill of rights |
| Assessment questions |
Democracy is the rule of the people by the people for the benefit of the people.
It allows the people to be directly involved in decision making on matters that affect their lives.
The opposite of democracy is dictatorship.
This is when the country is ruled by one person who does not take into account the feelings of the citizens of the country.

There are two major types of democracy namely:
See the image and table below:
| Direct Democracy | Representative Democracy |
|
- People are directly involved in making decisions - Everyone is consulted - Can also be called consensus |
- People elect representatives who speak for them - Representatives make decisions on other people's behalf - Kenya has this kind of democracy |
Representative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy.
Ballots are cast in favour of a candidate. See the image below
1. Parliamentary system is where the government is headed by a Prime Minister.
A parliament ensures that the country is governed according to the wishes of the people.
Below is a photo of the Kenyan parliament.
2. Presidential system is where the government is headed by a president who appoints members of cabinet and other government officials.
1. Justice: This means that the government should treat all people fairly.
2. Equity: All people should be treated equally regardless of their gender or social status.
3. Fairness: This means that there should be equity in sharing national resources. Some people should not have an advantage over others.
Remember that concepts like Justice, Equity and Fairness can be difficult to define and can mean different things to different people.
The cartoon below shows a good example of this.
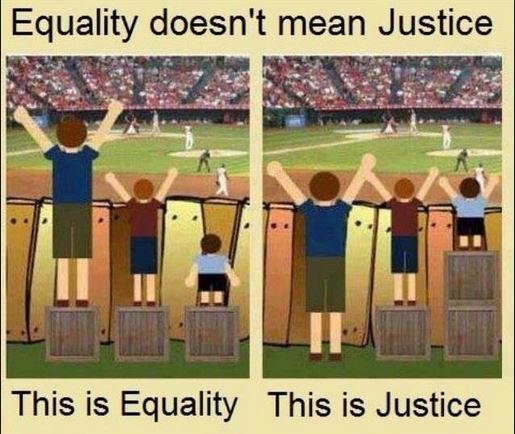
4. Rule of law: All citizens should be seen as being equal before the law.
If they commit an offence, they should be given equal treatment.
The law should not be bent to favour some people
5. Recognition of minority groups: No group of people should be ignored no matter how few they are.
Everybody should be listened to and heard by the government
6. Respect of human rights: All citizens should know their rights and make sure that they are respected.
They should speak out if they feel their rights are being abused.
Political parties are one way through which people can participate in political activities.
Below are some ways in which they can do this:
They also take back people’s views on the ideas discussed.

The image below show one of the World's dictators:

Human rights are contained in the constitution of Kenya.
The rights of citizens are sometimes called freedoms.
The following are the rights and freedoms of Kenya citizens according to the constitution.
Every citizen has the right to live.
This is also called freedom of speech.
This means people are free to give their opinion on a given issue either through writing or by word of mouth.
This means that a person is free to join any organisation or other people or groups of people and should not be forced to join any of them unwillingly.

5. Freedom of assembly:
This means people are free to hold meetings without interference from others.
This means that a person is free to become a member of any religion in Kenya.
This means if a person is taken to court; the trial must be done without showing hatred or favour.
This means that a person must not be arrested unless one has committed an offence.
This means that a person is free to move from one part of Kenya to another and to go out of Kenya and come back without being stopped by anyone.
Every Kenyan citizen is free to make political choices.
Every Kenyan citizen has a right to access information held by the state or by another person.
The section of the constitution that outlines the human rights is called the Bill of Rights.
Respecting Human Rights is a key part of the Kenyan Constitution.
Here is a picture of former President Kibaki holding the newly signed constitution in 2010.

People with special needs have the right to:

People with special needs have the responsibility to:
Abuse of human rights is denying others their rights and freedom.
When we use our rights and freedoms to offend others, then we are abusing those rights and freedoms.
Examples are: