- It is in the former Rift Valley Province of Kenya. It was created from the former Kericho district through Kenya gazette supplement no. 53 of 1992.
- It has a population of 724,186 and an covers an area of 1,630.0 km2
Bomet Central Constituency
Bomet East Constituency
Chepalungu Constituency
Sotik Constituency
Konoin Constituency
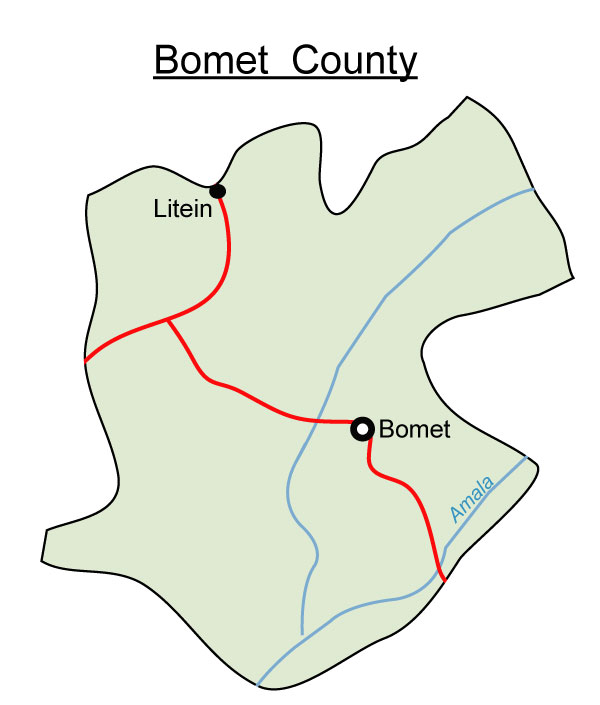
Rivers
Hills
Plains
Valleys
Bomet Game Reserve

Map distribution of physical features
Areas of high population density
Areas of low population density
Food
Dressing
Traditional Kipsigis dressing consisted of skins of either domestic or wild animals. Earings were worn for both genders, including heavy brass coils that made the earlobe stretch down almost to the shoulder.
Songs and dances
They made drums and other musical instruments from animal products. Drums were made from cattle skin. Cattle horns were also used as an instrument. They blew it and it produced a loud sound.
Music was used to celebrate special occasion in the society. Ceremonies like marriage, initiation, birth of a new born baby and harvest were all followed by vigorous song and dance. It was a way of thankgiving and appreciation.
- They had healers specifically for this reason.
- This gift was inherited from father to son.
- The healers had wide knowledge on plants and their effect. This knowledge is what was required in healing.
- They also practiced spiritual ways of healing like offering sacrifices and prayer.
A typical kipsigis has four names. According to Kipsigis names were given at birth, as individual matures, during initiation and has he/she marries. The name carries both the culture and identity of the person. The cultural name tells where they belong.
Keeba tuum, which was the initiation period, was the most important event in the life of the Kipsigis and the Kalenjin as a whole. Initiation rites for both male and female extended over a period of months and were very involved. Initiation was about rites of circumcision and also initiation into the secret rituals of the tribe and the teachings of tribal customs. The months the initiate spent in camp were a time of training for adulthood. It was almost like being in school for that period of time.
Kipsunde oieng harvest ceremony was held in October to mark the special occasion. Music and dance was used to help in celebrating the event as a sign of thank giving.
It was used to mark important ceremonies in the community. Besides funeral services the rest were followed by music and dance. Different songs were sung for different occasions. They had songs for war, harvest and birth of a child. Different songs had different purposes and different singing ways.
Bomet town is the area known for cash crops.
NB: details of breeds are not required
Areas where fishing is practiced
Fishing in bomet is mainly done in the rivers for local consumption. These rivers are:
Major forests
The types wildlife
The game parks and reserves
The major tourist attractions
The products of traditional industries