Lamu County
Introduction
Lamu County is located in the Northern Coast of Kenya and is one of the Six Coastal Counties in Kenya. It borders Kilifi County in the south west, Garissa County to the north, Republic of Somalia to the north east and the Indian Ocean to the South. Lamu is rich in minerals like titanium, salt, limestone, coral stones and sand. There is titanium mining and on-going exploration for oil and gas in Pate Island.
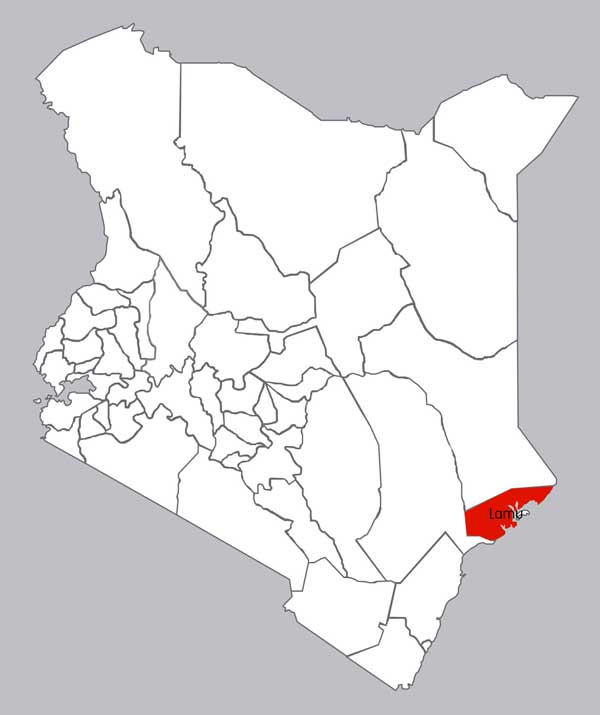
Constituencies
It consist of 2 constituencies
- Lamu West
- Lamu East
Physical features
Rivers
- Dodori River
- Tana river
- Lake Kenyatta
Lakes
- Lake Kenyatta / Lake Mukunganya
- Lake MOA
Hills
Plains
- Coastal plains
- Island plains
- Dodori River plain
Importance of physical features
- Tourist attraction
- Religious responsibility
- Source of water for the region
Main types of natural vegetation
- Woodland Scrubland System (Boni, Lunghi, Dodori )
Importance of vegetation
Map of the Distribution of natural vegetation
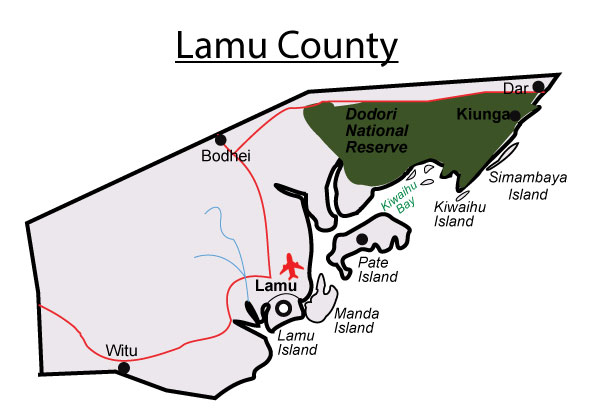
People and population
Language groups
- The people of Lamu are part of the Swahili people of east coast of Africa, found in the east coast of Kenya, Tanzania and Mozambique. The Swahili population of Lamu island and the mainland is a mixture of many groups: Bajunis, Arabs, Somalis and Indians.
Areas of high population density
- Lamu town has the most population in the region
Social relation and cultural activity
The traditional way of life
Food
The Swahili's staple food is of Arabic descent, and most of their cooking is rich in spices. Popular Swahili cuisine includes pilau and wali (rice cooked in coconut milk) served with a thick meat stew or fish. The Swahili tribe eats a lot of different grains, vegetables and fruits, including beans, peas, tomatoes, potatoes, okra, kale, spinach, mangoes, coconut and bananas. Goat meat and chicken are traditionally served during special occasions.
Dressing
The traditional attire of a Swahili man is a long white (or beige) robe (or kaftans) known in Swahili as a kanzu and a small, white, rounded hat with elaborate embroidery. Swahili women dress in long black dresses called buibui, and cover their heads with a black cloth, known as a hijabu.
Songs and dances
Swahili music, Taarab, is poetically very rich. The traditional Taarab rhythm is a slow beat that borrows heavily from Indian and Arabic melody. Chakacha is another authentic Swahili music genre with a faster tempo than Taarab.
Traditional medical practices
There are several different kinds of Swahili healing specialists including scholars/teachers, diviners and traditional healers.
Ceremonies and festivals held
Ceremonies
Naming mostly reflected the circumstances at the time of birth.
There were no specific rites of passage of the Swahili people
Festivals
Swahili music, is called Taarab. The traditional Taarab rhythm is a slow beat. Which is a slow beat with slow movements of the waist by women.
Resources and economic ativities
Agriculture
Main cash crops and food crops grown
- The cash crops are cotton, simsim, coconut, cashew nuts, bixa, vegetables and mangoes.
- The main food crops grown include maize, sorghum, cow pees, green grams, lablab, rice and cassava.
Areas where the cash crops are grown
- Mpeketoni
- Tana basins
- Lake Kenyatta /Lake Mukunganya
- Lake MOA areas
Types of livestock kept
- Cattle
- Sheep
- Goat
- Donkeys
- poultry
Fishing
Areas where fishing is practiced
- Kiwayu is the main fishing ground in the area.
Forestry
Major forests
Wildlife and Tourism
Types wildlife
- Tropical commercial fish
- Crocodiles and hippos
- 7000 species of plants, along with at least 2000 fungi and bacteria.
Game parks and reserves
- Lamu Game Reserve
- Kiunga Marine National Park
Major tourist attractions
- Manda island
- The majlis
- Lamu Fort
- Lamu Museum
Industries
Traditional industries
- Fishing industries
- Agriculture industries
Trade
Major trading centers
- Lamu town is the main town and the major trading center in the county


