Mandera County
Introduction
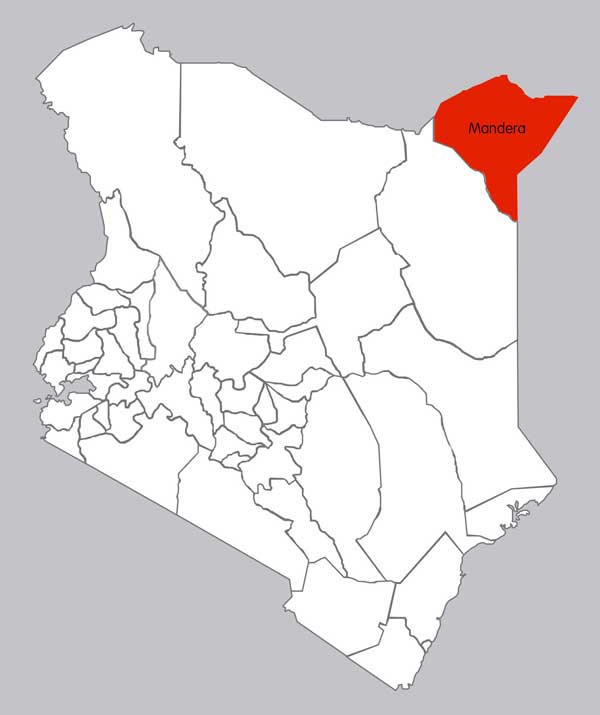
Mandera County is a county in the former North Eastern Province of Kenya. Its capital and largest town is Mandera. The county has a population of 1,025,756 (2009 census) and an area of 25,797.7 km².
Constituencies
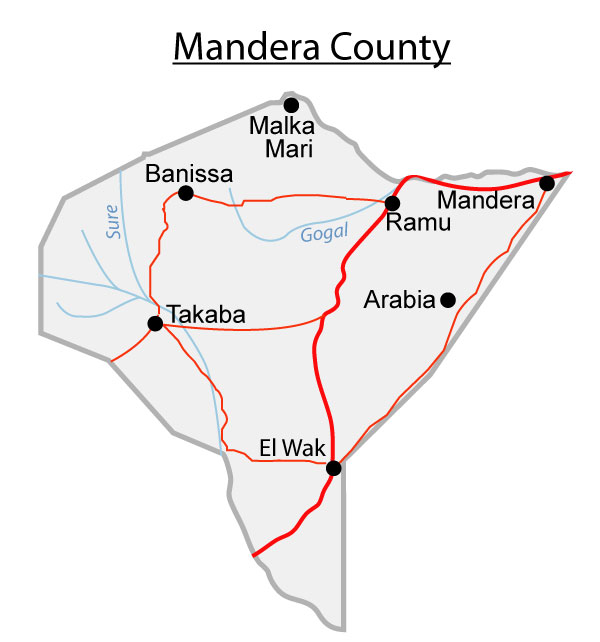
It consists of 6 constituencies
- Mandera South Constituency
- Mandera West Constituency
- Mandera East Constituency
- Mandera North Constituency
- Banisa Constituency
- Lafey Constituency
Physical features
Rivers
Lakes
Mountains
Hills
- Taita Hills
- Sagara Hills
- Hiils of Mandera
Plains
- White Plains
- Awara plains
Valleys
- Sun Valley
- Mandera hills and valleys
Importance of physical features
- Tourist attraction
- Some physical features like mountain and hills tops were used for spiritual purposes
- Some like rivers provide water to the semi-arid area
Natural vegetation
Importance of vegetation
- Vegetation prevents soil erosion in the area
- Source of food to the people and animals in the area
- Natural habitat to birds and animals
Map of the Distribution of physical features
People and population
Language groups
- The Somalis are the dominat language group in the area
Areas of high population density
The areas with a high population are:
- Mandera South Constituency
- Mandera West Constituency
- Mandera East Constituency
Areas of low population density
- Banisa Constituency and Lafey Constituency are the areas with the least population
Social relations and cultural activities
Traditional way of life
Food
Since many Somalis are nomads, back home they often ate a popular type of jerky called otka - preferably camel meat that is dried and then fried in butter and spices. Its preparation allowed the meat to be preserved for a long time, which made it ideal to take on long trips.
Dressing
An outfit commonly worn by Somali men is a white cotton sheet wrapped around them as a skirt and another white piece used as a shawl. Most Somali women wear full-length dresses that come in a variety of styles.
Songs and dances
Dhaanto is a style of traditional Somali music and folk dance it was sung during war mainly on horse backs to raise the spirits of the warriors.
Traditional medical practices
The Somalis had traditional healers in every community responsible for the various health issues. They were widely respected in the community. They used three methods of healing:
- Cauterization- nails, a piece of palm or wood were used to burn out a disease. They believe diseases and fire cannot stay together.
- Traditional bone setting cured using plants which was widely considered
- Scarification –performing body cuts to draw out bad blood
They also used religious acts to heal.
Ceremonies and festivals held
Ceremonies
Somali names have three parts. The first name is the given name, and is specific to an individual. The second name is the name of the child's father, and the third name is the name of the child's paternal grandfather. Thus siblings, both male and female, will share the same second and third names. Women, when they marry, do not change their names. By keeping the name of their father and grandfather, they are, in effect, maintaining their affiliation with their clan of birth.
When a boy reaches adolescence his arm (triceps) is struck forcefully by an older gelfie. The point of this painful initiation ceremony is to make the lads triceps bulge out, thus this shows his entrance into manhood.
Festivals
Neeroosh celebrates the beginning of the solar year in Somalia and Somaliland. Somalis and Muslim use the solar calendar to make decisions about religious days and harvest times. The festival is known as the Festival of Fire where local people build huge bonfires, splash water on each other and dance to welcome the arrival of summer.
Somali songs are pentatonic. That is, they only use five pitches per octave in contrast to a heptatonic (seven note) scale such as the major scale.
Resources and econimic activities
Agriculture
Main cash crops and food crops grown
- Fruits(Mangoes, Pawpaws, water melons, guavas, lemons and bananas)
- Maize
- Beans
- Cotton
- Pyrethrum
Areas where the cash crops
Types of livestock kept
Fishing
Areas where fishing is practiced
- Fishing is practiced in fish ponds. Mandera is an arid region with no water bodies
Forestry
Major forests
- Mandera is an arid area. Fishing sites are a man made in small scale. Fishing is practiced in fishing ponds
Wildlife and Tourism
Types of wildlife
- Giraffe
- Buffalo
- Zebra
- Elephant
Game parks and reserves
- Chacnabole conservancy
- Malka Mari National Park
Major tourist attractions
- Chacnabole conservancy
- Malka Mari National Park
Industries
Traditional industries
- Trade- animal products like milk, meat, cloths
- Agriculture –farm products
Trade
Major trading centres
- Mandera town is the main trading center


