There are many fishing villages along the Coast of Kenya and Tanzania. The main fish caught in the ocean are king fish, parrot fish, oysters, prawns, shrimps, lobsters, turtles, sharks, kingfish and whales.
Large scale commercial fishing is carried out in the Indian Ocean as well as subsistence fish farming. This fish is sold to major towns along the Coast as well as inland. These towns include: Mombasa, Kisumu, Nakuru and Eldoret, besides the local villages along the Coast.
Fishing is the catching of fish from lakes, rivers, swamps or the sea by fishermen. It is an important economic activity. There are two types of fishing grounds in Africa.
These are:
The table below shows the main fishing grounds in Africa.
Below are examples of large scale or commercial methods of fishing.
In this method, a boat pulls a bag or a cone-shaped net in water. As the boat is pulled, fish get into the net and are trapped. This method is mostly used in deep fishing grounds. This method is not recommended in inland fishing ground because it catches small fish therefore exploiting them.
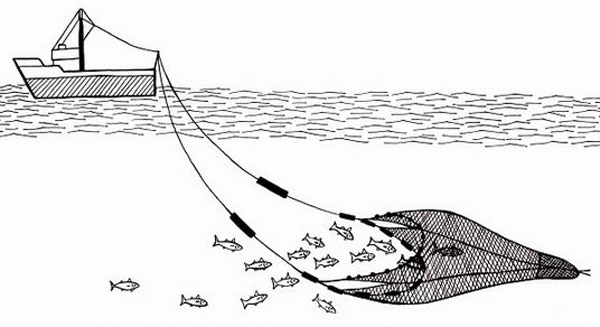
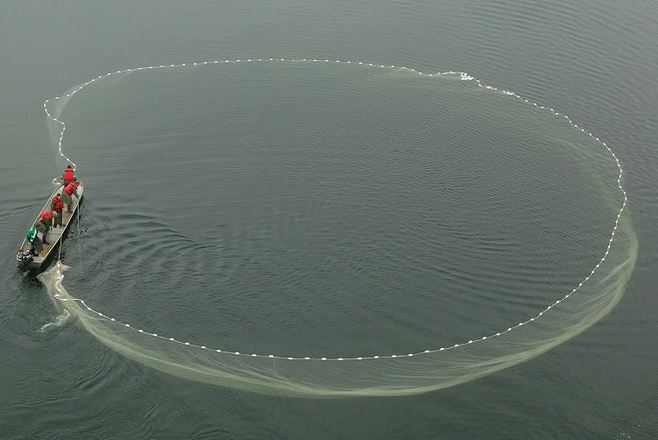
A flat net with floaters on top and weights at the bottom is tied on the boats. The two boats pull the nets as they move towards one another trapping fish in the net. This method is used in shallow fishing grounds.

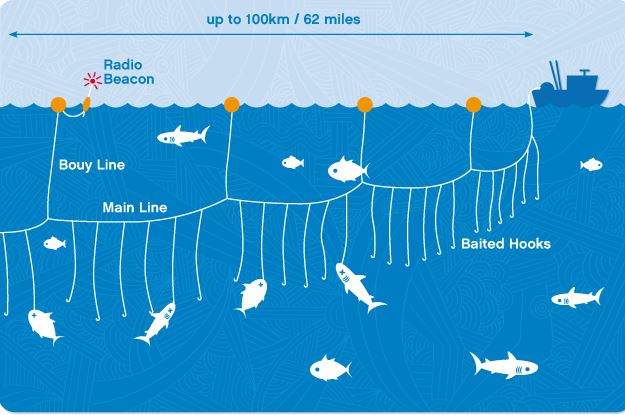
In this method, hooks are fixed on a line and a bait is fixed on the hooks. A boat pulls the line with a bait in a water body. Fish are trapped by the hooks as they try to eat the bait.
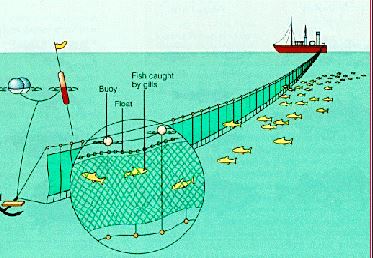
In this method, a long net with floaters on top and weights at the bottom is placed across a river, lake or sea. This net traps fish.
Both traditional and modern methods are used to preserve fish in Kenya. These methods include the following:
1. Fishing has led to the development of fish industries and the related industries like:
2. It generates employment, especially in the actual fishing, preservation, processing and marketing of products.
3. It is an important source of food protein.
4. Fish products are exported to earn the country foreign exchange.
5. It is used as a raw material for making fertiliser and utensils.
6. It has contributed to improving the standards of living of the fishermen and those working in the fishing and related industries.
7. Fishing leads to improvement of transport and communication networks.
8. Some fishing villages develop into towns and urban centres.
9. Fish oil is used in the manufacture of medicine.
10. Sport fishing is at ourist attraction which earns the country foreign exchange
Water hyacinth on inland lakes like Victoria and Naivasha makes it difficult for boats to move. The weed is also responsible for the reduced size of the lakes.
Most fishermen use traditional methods of fishing that do not catch much fish. They earn little money from fishing.
Over-fishing of some fish species like tilapia on Lake Victoria may make the species disappear.
Pollution of lakes and seas poisons and kills fish.
Lack of modern storage facilities like refrigerators.
There is a limited market for fish, as many communities living away from water bodies are not used to eating it.
Production is on a small scale.
Uses more traditional or subsistence methods.
Does not require a lot of capital to start ponds.
There is little control over the quality of the water in the ponds.
Fish mainly comes from inland fishing grounds.
Co-operatives help to fillet fish and help the farmers to market it. However, they do not have enough funds.
It is leading producer of fish under fish farming
Uses more modern technology.
It is very capital intensive
Fishing is mainly done for export.
There is great control over the quality of water used in fish farming.
Fish is mainly from the sea
Government offers loans to farmers to develop their fish farming ponds and facilities.
Fish farming is the keeping of fish in ponds, rivers and lakes. The practice is also called aquaculture. The places where these fish are hatched are called hatcheries. In Kenya, hatcheries are mainly found at Sagana, Kisumu, Lake Naivasha and around Lake Baringo.
The most popular species bred in the ponds in Kenya are the tilapia, the black bass and black trout. In developed countries like Japan, fish farming is bred in enclosures, which are then arranged into a larger pond. These enclosures are called hapas. Fish farming areas include Sagana, Nyeri, Bamburi, Kisii, Kibos, Rango, Homabay and Kakamega.