Nutrients are the components that are in the food that helps the body to grow, have strength and be strong.
Different nutrients are found in different food groups.
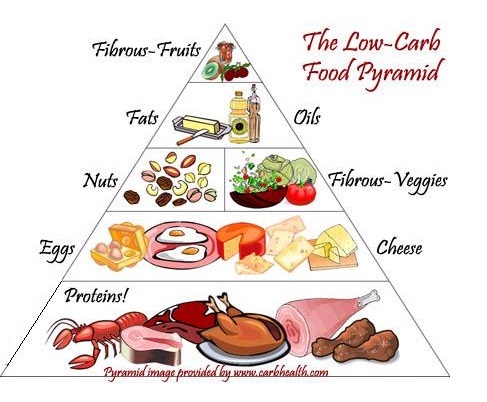
1. Carbohydrates.
2. Fats and oils.
3. Proteins.
4. Vitamins.
5. Minerals.
These nutrients perform different functions in the body.
These give the body energy to function, work, and play.
They are found in energy-giving foods, for example, ugali and rice.

Proteins help in bodybuilding, growth, and repair of the body.
They are found in bodybuilding foods like meat and fish.
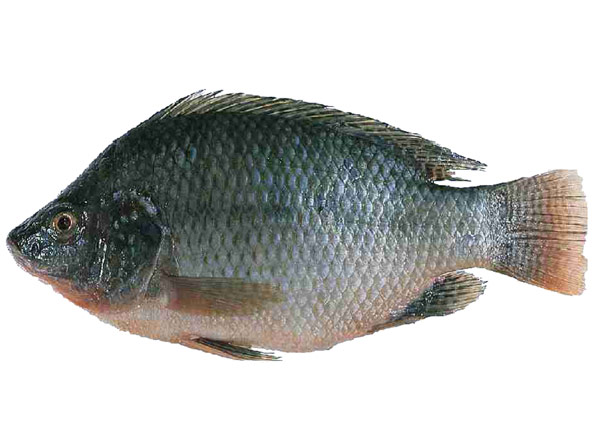

Vitamins help in protecting the body against diseases.
They also help the body to heal fast.
Vitamins are found in protective foods like vegetables and fruits.
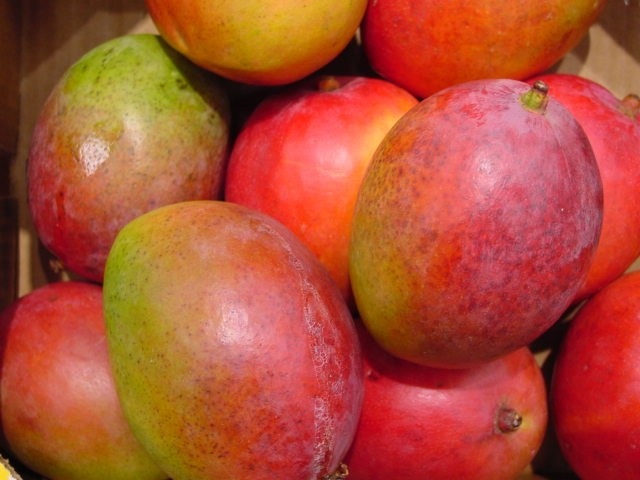

Minerals help in forming strong bones and teeth.
Examples of minerals are iron, calcium and phosphorous.


These provide the body with energy which provides warmth.
Fats may be gotten from various foods like nuts, fruits, and animal products.

Water is very essential in the body and should be taken every day.
One needs to take six to eight (6-8) glasses of water every day.
Water can be taken plain or in fruits like oranges.
Fibres are found in vegetables.
They are also called roughages.
Water and fibres help in digestion and in making it possible to pass stool.
A meal that has carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins, minerals, fats and oils, water and fibres is called a balanced diet.
Some people in the home may have special problems and therefore may need special handling when it comes to the diet or meals.
Such groups, for example, are:
Pregnant mothers are a special group since they carry offspring in their wombs.
Pregnant mothers need to eat food that caters for two:
the child in the womb and herself.
The two also require different nutrients in different amounts.


However, too much of carbohydrates are dangerous because she might become overweight and suffer from obesity which may complicate birth.

She should take at least two litres of liquids per day.
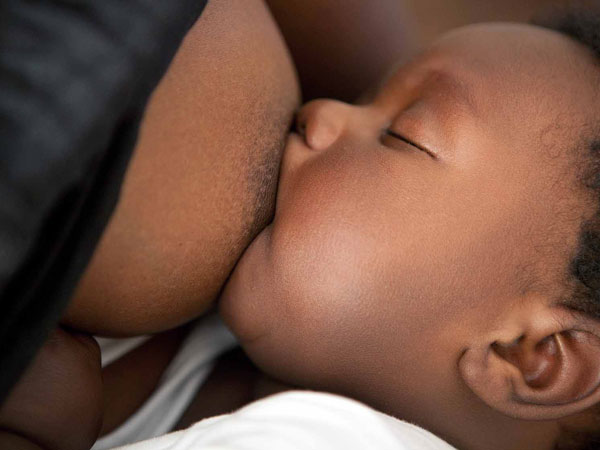
A lactating mother is a breast feeding mother.

She needs a special diet to cater for her needs and to her help produce sufficient breast milk to feed and satisfy the new born baby who fully relies on breast milk.
Let’s look at the nutritional requirements for a lactating mother.
A lactating or breastfeeding or nursing mother needs a diet with:
Colostrum helps to protect the child from diseases.
• Proteins help the mother to build and repair tissues that were affected by pregnancy and birth.
• Fats and carbohydrates: the lactating mother needs a diet with carbohydrates to provide energy for her to breastfeed the baby, move around and for the body to do its normal functions.
An infant is a child between birth and two years.

This is a small child who might not be able to feed on the normal family meal because the digestive system is not developed enough to cope.
The infant may also have no teeth.
What are the nutritional requirements for an infant?
1. Breast milk is the best food for an infant since it forms a whole meal.
Milk is a balanced diet as it contains proteins, carbohydrates, fats, minerals and vitamins.
It also has lots of water, which the infant needs.
These provide more proteins for body building and growth, and carbohydrates for energy for movement and body functions.